loglama
LogLama - The Primary Service for the PyLama Ecosystem
PyLama Ecosystem Navigation
| Project | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
| LogLama | Centralized logging and environment management | GitHub · PyPI · Docs |
| GetLLM | LLM model management and code generation | GitHub · PyPI · Docs |
| DevLama | Python code generation with Ollama | GitHub · Docs |
| APILama | API service for code generation | GitHub · Docs |
| BEXY | Sandbox for executing generated code | GitHub · Docs |
| JSLama | JavaScript code generation | GitHub · NPM · Docs |
| JSBox | JavaScript sandbox for executing code | GitHub · NPM · Docs |
| SheLLama | Shell command generation | GitHub · PyPI · Docs |
| WebLama | Web application generation | GitHub · Docs |
Author
Tom Sapletta — DevOps Engineer & Systems Architect
- 💻 15+ years in DevOps, Software Development, and Systems Architecture
- 🏢 Founder & CEO at Telemonit (Portigen - edge computing power solutions)
-
🌍 Based in Germany Open to remote collaboration - 📚 Passionate about edge computing, hypermodularization, and automated SDLC
Support This Project
If you find this project useful, please consider supporting it:
📚 Project Documentation Menu
- Project Overview (README)
- Feature Command Comparison
- Feature Comparison
- Component Integration Guide
- Ecosystem Integration
- Technical Diagrams
- Contributing Guide
- Badge Reference
- Examples
- Scripts Guide
- Usage Guide for LogLama-Grafana
See also: Full Command Comparison Table Feature Comparison Examples Component Integration Guide Ecosystem Integration Technical Diagrams Contributing Guide
LogLama is the foundational primary service for the entire PyLama ecosystem, managing centralized environment configuration, dependency validation, service orchestration, and comprehensive logging across all components. As the first service to start, LogLama ensures all components have the correct configuration and dependencies before they run. It provides a unified logging and environment solution that can be integrated into any application or programming language, serving as the backbone of the PyLama architecture.
📁 Folder Structure
loglama/
├── examples/
│ ├── loglama-grafana/
│ ├── multi_component_example/
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── bash_example.sh
│ ├── basic_python_example.py
│ ├── multilanguage_examples.py
│ ├── devlama_integration_example.py
│ ├── simple_bash_example.sh
│ └── ...
├── loglama/
│ ├── api/
│ ├── cli/
│ ├── collectors/
│ ├── config/
│ ├── core/
│ ├── db/
│ ├── decorators/
│ ├── diagnostics/
│ ├── formatters/
│ ├── handlers/
│ ├── middleware/
│ ├── scripts/
│ ├── utils/
│ └── web/
├── scripts/
│ ├── MIGRATION_GUIDE.md
│ ├── README.md
│ └── ...
├── tests/
│ ├── ansible/
│ ├── integration/
│ └── unit/
├── logs/
├── Makefile
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
├── COMMANDS_COMPARISON.md
├── COMPARISON.md
├── COMPONENT_INTEGRATION.md
├── ECOSYSTEM_INTEGRATION.md
├── TECHNICAL_DIAGRAMS.md
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
└── BADGE.md
Makefile Commands
LogLama provides a comprehensive Makefile to streamline development, testing, and deployment. Below are the main targets and their descriptions:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
make setup |
Set up the project (create venv and install dependencies) |
make venv |
Create a Python virtual environment |
make install |
Install dependencies |
make test |
Run all tests (unit + integration) |
make test-unit |
Run unit tests |
make test-integration |
Run integration tests |
make test-ansible |
Run Ansible-based tests |
make lint |
Run linting checks (flake8 + mypy) |
make lint-no-mypy |
Run linting checks (flake8 only) |
make format |
Format code (black + isort) |
make build |
Build the package with Poetry |
make check-publish |
Check if the package is ready for publishing |
make publish-test |
Publish to TestPyPI |
make publish-dry-run |
Dry run of publishing process |
make publish |
Publish to PyPI (production) |
make run-api |
Start the API server |
make web |
Start the web interface |
make run-cli |
Start the CLI |
make run-example |
Run the example application |
make view-logs |
View logs in the web interface |
make run-integration |
Integrate LogLama into all components |
make run-examples |
Run all multi-language examples |
make run-shell-examples |
Run shell examples |
make clean |
Clean up generated files |
make help |
Show all available Makefile commands |
You can override variables such as PORT, HOST, LOG_DIR, and DB_PATH when running commands. For example:
make web PORT=8081 HOST=0.0.0.0 LOG_DIR=./logs DB_PATH=./logs/loglama.db
Docker Compose: LogLama + Grafana
You can run LogLama together with Grafana for log visualization using Docker Compose. See examples/loglama-grafana/ for a ready-to-use setup.
Quick Start
cd loglama/examples/loglama-grafana
# Build LogLama Docker image if not available
# docker build -t loglama:latest .
docker compose up -d
- LogLama web: http://localhost:5000
- Grafana: http://localhost:3001 (default: admin/admin)
Grafana Integration
- Use the SQLite datasource plugin to connect to LogLama’s SQLite DB (
/logs/loglama.db). - For file-based logs, use Loki or a sidecar to stream logs.
- Adjust volume mounts and permissions so Grafana can access the logs/DB.
Cleanup
docker compose down -v
| Feature | Example Command(s) |
|---|---|
| Centralized Env Management | python -m loglama.cli.main env |
| Dependency Validation | python -m loglama.cli.main check-deps |
| Service Orchestration | python -m loglama.cli.main start-all |
| Multi-output Logging | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --output console,file,db |
| Structured Logging | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --format structured |
| Context-aware Logging | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --context user_id=123 |
| Log Rotation/Backup | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --rotate |
| JSON/Colored Formatting | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --format jsonpython -m loglama.cli.main logs --format color |
| Bash Integration | bash examples/simple_bash_example.sh |
| Multi-language Support | python examples/multilanguage_examples.py |
| Web Interface | PYTHONPATH=. python loglama/cli/web_viewer.py --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8081 --db ./logs/loglama.db |
| Real-time Dashboard | (Open the web interface, real-time updates are visible in browser) |
| Log Filtering/Pagination | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --level WARNING --page 2 --page-size 50 |
| Export Logs (CSV) | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --export csv --output-file logs.csv |
| RESTful API | curl http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/logs |
| CLI Tools | python -m loglama.cli.main --help |
| Unit/Integration Tests | pytest tests/ |
| Auto-diagnostics/Repair | python -m loglama.cli.main diagnose |
| Health Checks/Reports | python -m loglama.cli.main stats |
| Integration Scripts | python examples/devlama_integration_example.py |
| Cluster/K8s Support | kubectl apply -f k8s/loglama-deployment.yaml |
| Grafana/Loki Integration | docker-compose -f examples/loglama-grafana/docker-compose.yml up |
| Prometheus Integration | (See Prometheus integration guide) |
| Context Capture Decorators | (Use @loglama.capture_context in your Python code) |
| Customizable via Env Vars | export LOGLAMA_DB_PATH=./logs/loglama.dbpython -m loglama.cli.main logs |
| Production DB Support | python -m loglama.cli.main logs --db postgresql://user:pass@host:5432/loglama |
| Eliminate Duplicated Code | (Follow LogLama integration patterns and shared utils) |
For advanced setups (scalable clusters, Prometheus, Loki, etc.), see the example docker-compose.yml and main documentation.
Scalable Cluster Deployment Example
LogLama can be deployed in a scalable cluster using Docker Compose with multiple replicas. This allows you to handle higher loads and ensure high availability.
Example: Scaling LogLama with Docker Compose
Below is an example docker-compose.yml snippet to run multiple LogLama instances behind a load balancer (e.g., Nginx) and connect to a shared SQLite database volume:
version: '3.8'
services:
loglama:
image: loglama:latest
deploy:
replicas: 3 # Number of LogLama instances
volumes:
- ./logs:/logs
- ./loglama.db:/logs/loglama.db
environment:
- LOGLAMA_DB_PATH=/logs/loglama.db
- LOGLAMA_LOG_DIR=/logs
ports:
- "5000"
networks:
- loglama-net
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
ports:
- "5000:5000"
depends_on:
- loglama
networks:
- loglama-net
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
ports:
- "3001:3000"
volumes:
- ./logs:/logs:ro
- ./loglama.db:/logs/loglama.db:ro
networks:
- loglama-net
networks:
loglama-net:
driver: bridge
Key Points:
- The
loglamaservice is scaled to 3 instances. Adjustreplicasas needed. - A load balancer (Nginx) routes requests to all LogLama instances.
- Logs and the SQLite database are stored on shared volumes for consistency.
- Grafana can read from the shared database or logs for visualization.
Note: For production, consider using PostgreSQL or another production-grade database for concurrent writes, and externalize log storage (e.g., use Loki for log aggregation).
LogLama Functionality
LogLama provides a comprehensive set of features for centralized logging, environment management, and integration within the PyLama ecosystem and beyond. Below is a complete list of its core functionalities:
- Centralized Environment Management
- Loads and validates environment variables from a single
.envfile - Ensures all components have correct configuration before startup
- Dependency validation and installation
- Service orchestration and startup order management
- Loads and validates environment variables from a single
- Advanced Logging System
- Multi-output logging: Console, file, SQLite database, and API endpoints
- Structured logging with
structlogsupport - Context-aware logging: Add context (user, action, etc.) to logs
- Simplified logging interface and decorators
- Log rotation and backup management
- JSON and colored log formatting
- Bash integration (log from shell scripts)
- Multi-language support (Python, JS, PHP, Bash, etc.)
- Web Interface
- Real-time log dashboard with filtering, pagination, and statistics
- Dark mode and responsive design
- Export logs to CSV
- RESTful API
- Query, filter, and manage logs programmatically
- Retrieve statistics and available log levels/components
- CLI Tools
- Command-line log viewing, filtering, and management
- Integration and diagnostic scripts
- Testing & Diagnostics
- Comprehensive unit, integration, and Ansible tests
- Auto-diagnostic tools and auto-repair decorators
- Health checks and diagnostic reports
- Integration & Extensibility
- Easy integration with other PyLama components
- Integration scripts for onboarding new projects
- Elimination of duplicated logging/environment code
- Cluster and Cloud-Native Support
- Docker Compose and Kubernetes deployment examples
- Scalable multi-instance support
- Grafana/Loki/Prometheus integration for dashboards and log aggregation
- Other
- Context capture via decorators and context managers
- Customizable via environment variables
- Support for production-grade databases (PostgreSQL, etc.)
Features
Centralized Environment Management
- Primary Service: Starts first and ensures all components have the correct configuration
- Centralized Configuration: Single
.envfile in thedevlamadirectory used by all components - Dependency Validation: Checks and installs dependencies before starting services
- Service Orchestration: Starts all services in the correct order with proper configuration
- Environment Validation: Ensures all required environment variables are set with proper values
- CLI Management: Comprehensive CLI for managing the entire PyLama ecosystem
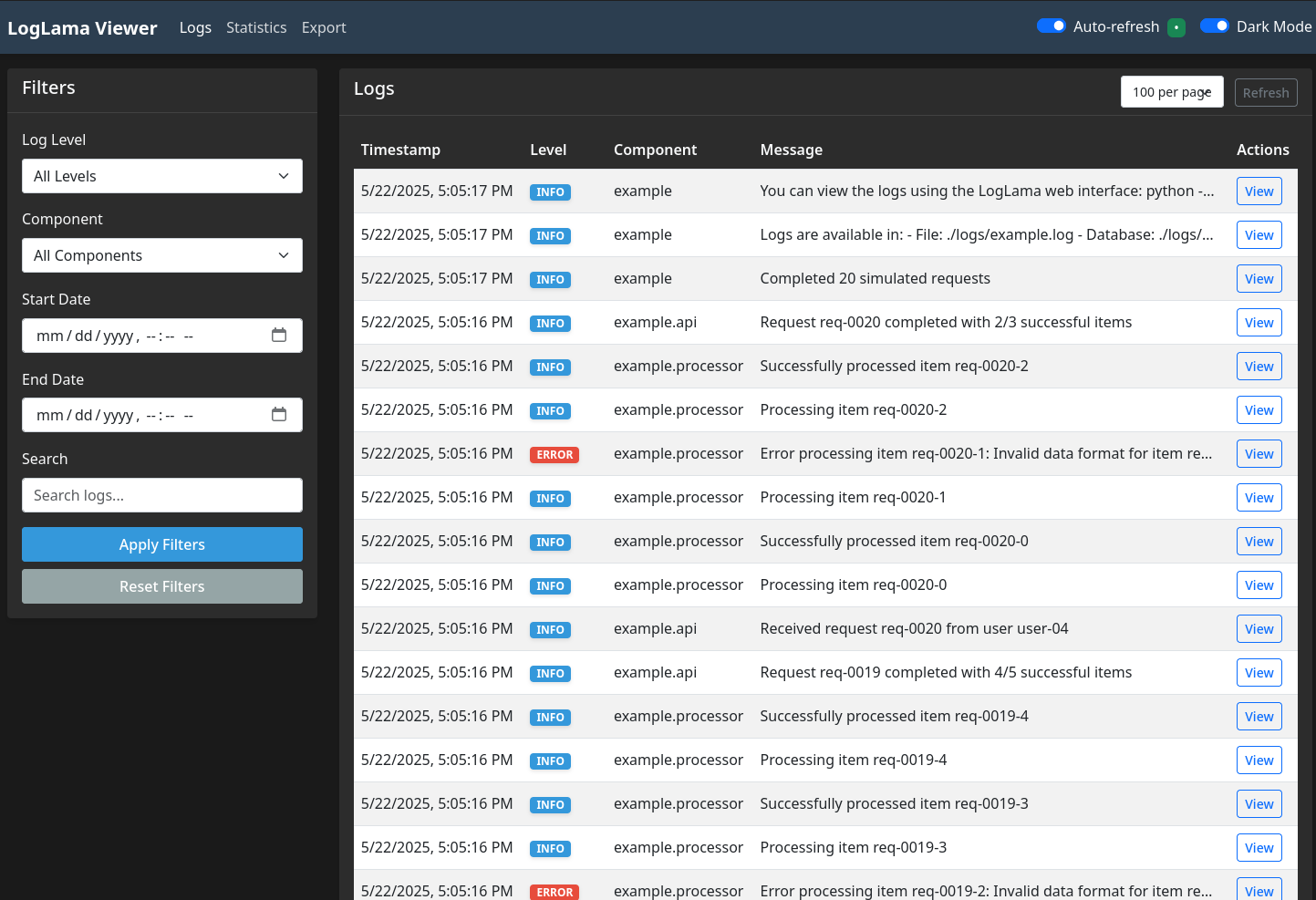
Advanced Logging System
- Multi-output logging: Console, file, SQLite database, and API endpoints
- Structured logging: Support for structured logging with
structlog - Context-aware logging: Add context to your logs for better debugging
- Simplified logging interface: Easy-to-use functions and decorators that automatically capture context
- Web interface: Visualize, filter, and query logs through an interactive web dashboard with dark mode and real-time updates
- RESTful API: Access and manage logs programmatically
- Command-line interface: Interact with logs from the terminal with rich formatting
- Custom formatters: JSON and colored output for better readability
- Enhanced handlers: Improved file rotation, SQLite storage, and API integration
- Bash integration: Log directly from bash scripts with simple functions
Integration & Extensibility
- Integration tools: Easily integrate LogLama into existing PyLama ecosystem components
- Comprehensive testing: Unit, integration, and Ansible tests for all components
- Multi-language support: Use LogLama from Python, JavaScript, PHP, Ruby, Bash, and more
- Environment testing: Ansible playbooks to test LogLama in different environments
Architecture and Integration
LogLama is the backbone of the PyLama ecosystem, providing centralized environment management, dependency validation, service orchestration, and a powerful logging system. All components integrate with LogLama for unified configuration and logging.
High-Level Architecture
graph TB
subgraph "PyLama Ecosystem"
subgraph "LogLama Primary Service"
LL_ENV[Environment Management] --> LL_DEP[Dependency Validation]
LL_DEP --> LL_ORCH[Service Orchestration]
LL_ORCH --> LL_COLL[Log Collector]
LL_COLL --> LL_DB[(LogLama DB)]
LL_DB --> LL_WEB[Web Interface]
LL_DB --> LL_CLI[CLI Commands]
end
subgraph "WebLama"
WL[Web UI] --> WL_LOG[Logging Module]
WL_LOG --> WL_FILE[weblama.log]
end
subgraph "APILama"
API[API Server] --> API_LOG[Logging Module]
API_LOG --> API_FILE[apilama.log]
end
subgraph "PyLama Core"
PL[Core Engine] --> PL_LOG[Logging Module]
PL_LOG --> PL_FILE[devlama.log]
end
subgraph "BEXY"
PB[Sandbox] --> PB_LOG[Logging Module]
PB_LOG --> PB_FILE[bexy.log]
end
subgraph "PyLLM"
PLLM[LLM Interface] --> PLLM_LOG[Logging Module]
PLLM_LOG --> PLLM_FILE[getllm.log]
end
%% Environment Management
LL_ENV -->|Configures| WL
LL_ENV -->|Configures| API
LL_ENV -->|Configures| PL
LL_ENV -->|Configures| PB
LL_ENV -->|Configures| PLLM
%% Dependency Validation
LL_DEP -->|Validates| WL
LL_DEP -->|Validates| API
LL_DEP -->|Validates| PL
LL_DEP -->|Validates| PB
LL_DEP -->|Validates| PLLM
%% Service Orchestration
LL_ORCH -->|Starts| WL
LL_ORCH -->|Starts| API
LL_ORCH -->|Starts| PL
LL_ORCH -->|Starts| PB
LL_ORCH -->|Starts| PLLM
%% Log Collection
LL_COLL --> WL_FILE
LL_COLL --> API_FILE
LL_COLL --> PL_FILE
LL_COLL --> PB_FILE
LL_COLL --> PLLM_FILE
end
Component Integration Points
All major ecosystem components (WebLama, APILama, PyLama Core, BEXY, PyLLM) integrate with LogLama by:
- Using the centralized
.envconfiguration - Logging to their own log files, which are collected by LogLama
- Supporting structured, context-aware logging for unified analysis
Technical Diagram
graph TB
subgraph "Primary Service"
LL[LogLama]:::primary
LC[Log Collector]:::collector
SC[Scheduled Collector]:::collector
DB[(LogLama DB)]:::storage
WI[Web Interface]:::interface
CLI[CLI Commands]:::interface
ENV[Environment Management]:::primary
DEP[Dependency Validation]:::primary
ORCH[Service Orchestration]:::primary
end
subgraph "Components"
WL[WebLama]:::component
AL[APILama]:::component
PL[PyLama]:::component
PB[BEXY]:::component
PLLM[PyLLM]:::component
end
LL -->|Starts First| ENV
ENV -->|Configures| WL
ENV -->|Configures| AL
ENV -->|Configures| PL
ENV -->|Configures| PB
ENV -->|Configures| PLLM
DEP -->|Validates| WL
DEP -->|Validates| AL
DEP -->|Validates| PL
DEP -->|Validates| PB
DEP -->|Validates| PLLM
ORCH -->|Starts| WL
ORCH -->|Starts| AL
ORCH -->|Starts| PL
ORCH -->|Starts| PB
ORCH -->|Starts| PLLM
WL -->|Generate Logs| LC
AL -->|Generate Logs| LC
PL -->|Generate Logs| LC
PB -->|Generate Logs| LC
PLLM -->|Generate Logs| LC
LC -->|Import Logs| DB
SC -->|Scheduled Import| LC
DB -->|Query Logs| WI
DB -->|Query Logs| CLI
classDef primary fill:#ff9,stroke:#f90,stroke-width:3px
classDef component fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
classDef collector fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
classDef storage fill:#bfb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
classDef interface fill:#fbb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
Comparison with Other Logging Systems
For a detailed comparison of LogLama with other logging systems (ELK, Graylog, Fluentd, Prometheus+Grafana, Sentry, Datadog), see COMPARISON.md or the summary below:
For detailed architecture and integration points, see the diagrams above and the COMPARISON.md.
Installation
pip install loglama
Or with additional features:
# Install with database support
pip install loglama[db]
# Install with web interface
pip install loglama[web]
# Install with all features
pip install loglama[all]
Quick Start
# Basic usage
from loglama import get_logger
# Get a logger
logger = get_logger("my_app")
# Log messages
logger.info("This is an info message")
logger.warning("This is a warning message")
logger.error("This is an error message")
# Log with context
from loglama import LogContext
with LogContext(user_id="123", action="login"):
logger.info("User logged in")
# Nested context
with LogContext(action="validate"):
logger.debug("Validating request data")
# Using the decorator
@capture_context(module="auth")
def authenticate_user(username):
logger.info(f"Authenticating user: {username}")
Configuration
LogLama can be configured through environment variables or a .env file. Copy the env.example file to .env and modify it as needed:
cp env.example .env
Key configuration options:
# Logging Configuration
LOGLAMA_LOG_LEVEL=INFO # Options: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL
LOGLAMA_LOG_DIR=./logs # Directory to store log files
LOGLAMA_CONSOLE_ENABLED=true # Enable console logging
LOGLAMA_FILE_ENABLED=true # Enable file logging
LOGLAMA_JSON_LOGS=false # Use JSON format for logs
LOGLAMA_STRUCTURED_LOGGING=false # Use structured logging with structlog
# Database Configuration
LOGLAMA_DB_LOGGING=true # Enable database logging
LOGLAMA_DB_PATH=./logs/loglama.db # Path to SQLite database
# Advanced Configuration
LOGLAMA_MAX_LOG_SIZE=10485760 # Maximum log file size in bytes (10 MB)
LOGLAMA_BACKUP_COUNT=5 # Number of backup log files to keep
# Web Interface Configuration
LOGLAMA_WEB_PORT=5000 # Web interface port
LOGLAMA_WEB_HOST=127.0.0.1 # Web interface host
LOGLAMA_WEB_PAGE_SIZE=100 # Number of logs per page in web interface
LOGLAMA_WEB_DEBUG=false # Enable debug mode for web interface
Environment variables are loaded automatically at the beginning of your application, before any other imports, to ensure proper configuration.
Usage Examples
Advanced Configuration
from loglama import configure_logging
# Configure logging with multiple outputs
logger = configure_logging(
name="my_app",
level="DEBUG",
console=True,
file=True,
file_path="/path/to/logs/my_app.log",
database=True,
db_path="/path/to/db/loglama.db",
json=True
)
# Now use the logger
logger.info("Application started")
# Using decorators for timing function execution
@timed
def process_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
# Using decorators for logging function calls with arguments and results
@logged(level="info", log_args=True, log_result=True, comment="Important calculation")
def calculate_value(x, y):
return x * y
# Combining decorators
@timed
@logged(comment="Data processing function")
def process_important_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
Using Context
from loglama import get_logger, LogContext, capture_context
logger = get_logger("my_app")
# Using the context manager
with LogContext(user_id="123", request_id="abc-123"):
logger.info("Processing request")
# Nested context
with LogContext(action="validate"):
logger.debug("Validating request data")
# Using the decorator
@capture_context(module="auth")
def authenticate_user(username):
logger.info(f"Authenticating user: {username}")
Using the CLI
# Start the CLI
make run-cli
# Or run directly
python -m loglama.cli.main
# View recent logs
loglama logs view --limit 10
# View logs by level
loglama logs view --level ERROR
# Clear logs
loglama logs clear
Using the Web Interface
# Start the web interface (new command)
make web
# Or run with custom port and host
make web PORT=8081 HOST=0.0.0.0
# Or use the CLI directly
loglama web --port 8081 --host 0.0.0.0
Then open your browser at http://localhost:8081 (or your custom port).
The web interface provides:
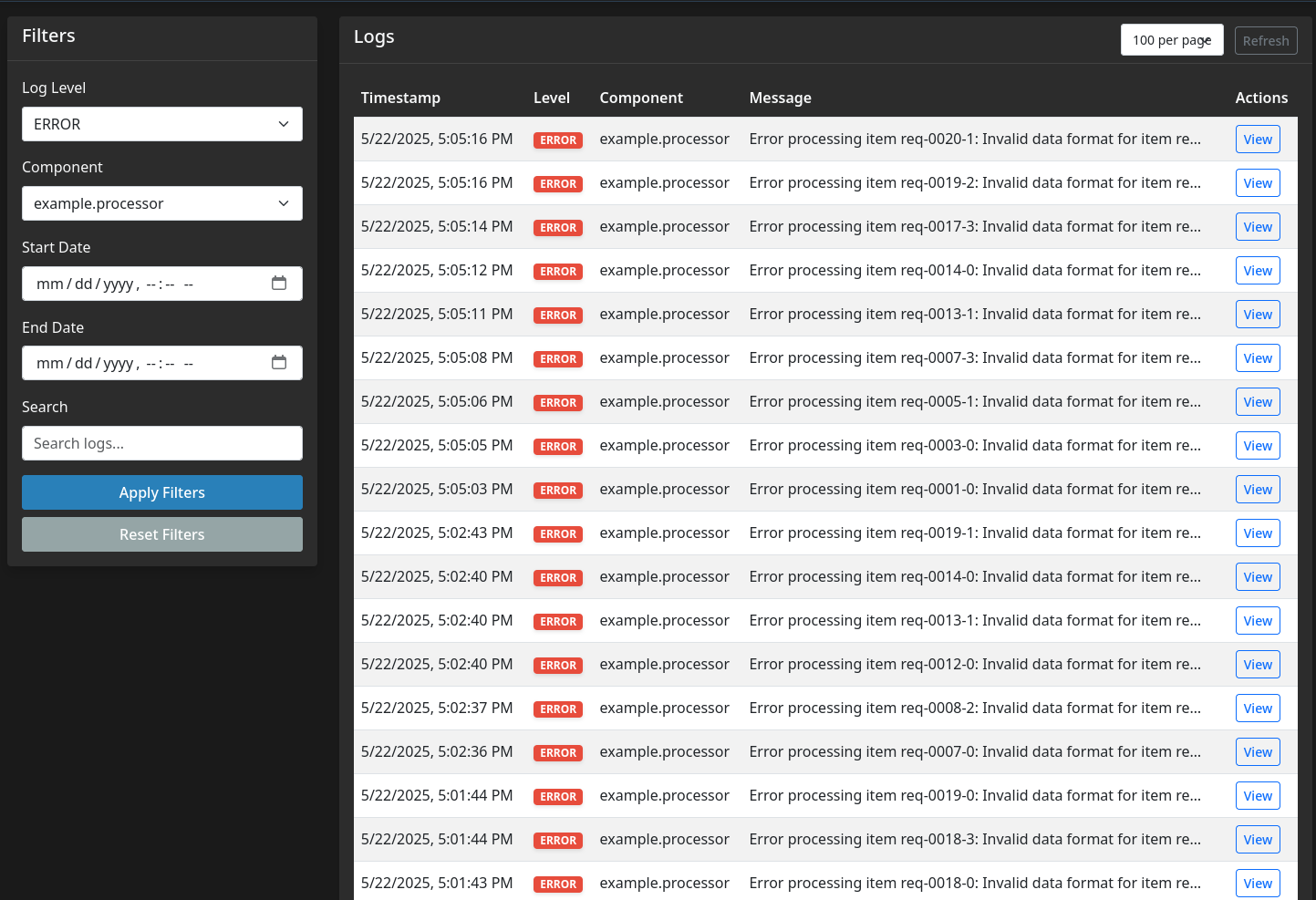
- Log Filtering: Filter logs by level, component, date range, and text search
- Pagination: Navigate through large log sets with pagination
- Statistics: View log statistics by level, component, and time period
- Log Details: View detailed information about each log entry, including context
- Real-time Updates: Auto-refresh to see the latest entries in real-time
- Dark Mode: Toggle between light and dark themes for better visibility
- Export: Export logs to CSV for further analysis
- Responsive Design: Works on desktop and mobile devices
Using the API
# Start the API server
make run-api
# Or run with custom port
make run-api PORT=8080 HOST=0.0.0.0
API endpoints:
GET /api/logs- Get logs with optional filtering- Query parameters:
level,search,start_date,end_date,component,page,page_size
- Query parameters:
GET /api/logs/{id}- Get a specific log by IDGET /api/stats- Get logging statistics (counts by level, component, etc.)GET /api/levels- Get available log levelsGET /api/components- Get available components (logger names)POST /api/logs- Add a new log (for external applications)
Simplified Logging Interface
LogLama provides a simplified logging interface that makes it easy to add logging to your applications without having to specify class names or contexts. The interface automatically captures context information and provides decorators for timing and logging function calls.
Python Usage
# Import the simplified interface
from loglama.core.simple_logger import (
info, debug, warning, error, critical, exception,
timed, logged, configure_db_logging
)
# Configure database logging (optional)
configure_db_logging("logs/myapp.db")
# Basic logging - automatically captures module, function, and line information
info("Starting application")
# Logging with additional context
info("Processing file", file_name="example.txt", file_size=1024)
# Using decorators for timing function execution
@timed
def process_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
# Using decorators for logging function calls with arguments and results
@logged(level="info", log_args=True, log_result=True, comment="Important calculation")
def calculate_value(x, y):
return x * y
# Combining decorators
@timed
@logged(comment="Data processing function")
def process_important_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
Bash Usage
# Source the helper script
source /path/to/loglama/scripts/loglama_bash.sh
# Basic logging
log_info "Starting script"
# Logging with different levels
log_debug "Debug information"
log_warning "Warning message"
log_error "Error occurred"
# Logging with a specific logger name
log_info "Processing started" "file_processor"
# Timing command execution
time_command "sleep 2" "Waiting for process"
# Setting up database logging
setup_db_logging "logs/bash_script.db"
# Starting the web interface for viewing logs
start_web_interface "127.0.0.1" "8081" "logs/bash_script.db"
Running the Examples
# Run the Python example
cd loglama
python examples/simple_python_example.py
# Run the Bash example
cd loglama
bash examples/simple_bash_example.sh
Multi-Language Support
LogLama can be used from various programming languages and technologies. Here are some examples:
JavaScript/Node.js
// JavaScript integration with LogLama
const { exec } = require('child_process');
class PyLogger {
constructor(component = 'javascript') {
this.component = component;
}
log(level, message, context = {}) {
const contextStr = JSON.stringify(context).replace(/"/g, '\"');
const cmd = `python3 -c "from loglama.core.logger import get_logger; import json; logger = get_logger('${this.component}'); logger.${level}('${message}', extra={'context': json.loads('${contextStr}') if '${contextStr}' else {}})"`;
exec(cmd);
}
debug(message, context = {}) { this.log('debug', message, context); }
info(message, context = {}) { this.log('info', message, context); }
warning(message, context = {}) { this.log('warning', message, context); }
error(message, context = {}) { this.log('error', message, context); }
}
// Usage
const logger = new PyLogger('my_js_app');
logger.info('Hello from JavaScript!', { user: 'js_user' });
PHP
<?php
// PHP integration with LogLama
class PyLogger {
private $component;
public function __construct($component = 'php') {
$this->component = $component;
}
public function log($level, $message, $context = []) {
$contextJson = json_encode($context);
$contextJson = str_replace('"', '\"', $contextJson);
$cmd = "python3 -c \"from loglama.core.logger import get_logger; import json; logger = get_logger('{$this->component}'); logger.{$level}('{$message}', extra={'context': json.loads('{$contextJson}') if '{$contextJson}' else {}})\""
;
exec($cmd);
}
public function info($message, $context = []) { $this->log('info', $message, $context); }
public function error($message, $context = []) { $this->log('error', $message, $context); }
}
// Usage
$logger = new PyLogger('my_php_app');
$logger->info('Hello from PHP!', ['user' => 'php_user']);
?>
Bash
#!/bin/bash
# Bash integration with LogLama
function pylog() {
local level=$1
local message=$2
local component=${3:-"bash"}
python3 -c "from loglama.core.logger import get_logger; logger = get_logger('$component'); logger.$level('$message')"
}
# Usage
pylog "info" "Hello from Bash!" "my_bash_script"
pylog "error" "Something went wrong" "my_bash_script"
Run the multi-language examples with:
# Run all multi-language examples
make run-examples
# Run shell examples specifically
make run-shell-examples
Integration with PyLama Ecosystem
LogLama is designed to work seamlessly with other components of the PyLama ecosystem. Use the integration script to add LogLama to any component:
# Integrate LogLama into all components
make run-integration
# Or run directly for a specific component
python scripts/integrate_loglama.py --component apilama
The integration script will:
- Create necessary directories and files
- Add logging configuration to the component
- Update environment variables in
.envand.env.examplefiles - Provide instructions for using LogLama in the component
Example integrations:
- WebLama: Track web requests and user interactions with context-aware logging
- APILama: Log API calls and responses with structured data for debugging
- BEXY: Track file operations and system events with detailed context
- PyLLM: Monitor LLM interactions and performance metrics
Example Application
LogLama includes an example application that demonstrates its features:
# Run the example application
make run-example
# View the generated logs in the web interface
make view-logs
The example application simulates a web service processing requests and demonstrates:
- Different log levels (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL)
- Context-aware logging with request IDs and user IDs
- Error handling and exception logging
- Structured logging with additional context fields
- Database logging for later analysis
Simplified Logging Interface
LogLama provides a simplified logging interface that makes it easy to add logging to your applications without having to specify class names or contexts. The interface automatically captures context information and provides decorators for timing and logging function calls.
Python Usage
# Import the simplified interface
from loglama.core.simple_logger import (
info, debug, warning, error, critical, exception,
timed, logged, configure_db_logging
)
# Configure database logging (optional)
configure_db_logging("logs/myapp.db")
# Basic logging - automatically captures module, function, and line information
info("Starting application")
# Logging with additional context
info("Processing file", file_name="example.txt", file_size=1024)
# Using decorators for timing function execution
@timed
def process_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
# Using decorators for logging function calls with arguments and results
@logged(level="info", log_args=True, log_result=True, comment="Important calculation")
def calculate_value(x, y):
return x * y
# Combining decorators
@timed
@logged(comment="Data processing function")
def process_important_data(data):
# Process data here
return result
Bash Usage
# Source the helper script
source /path/to/loglama/scripts/loglama_bash.sh
# Basic logging
log_info "Starting script"
# Logging with different levels
log_debug "Debug information"
log_warning "Warning message"
log_error "Error occurred"
# Logging with a specific logger name
log_info "Processing started" "file_processor"
# Timing command execution
time_command "sleep 2" "Waiting for process"
# Setting up database logging
setup_db_logging "logs/bash_script.db"
# Starting the web interface for viewing logs
start_web_interface "127.0.0.1" "8081" "logs/bash_script.db"
Running the Examples
# Run the Python example
cd loglama
python examples/simple_python_example.py
# Run the Bash example
cd loglama
bash examples/simple_bash_example.sh
Duplicate Code Elimination
One of the key benefits of LogLama is the elimination of duplicated logging code across projects. The integration script helps you remove redundant code related to:
- Environment variable loading: Standardized .env file loading
- Logging configuration: Consistent setup across all components
- Debug utilities: Common debugging functions and tools
- Context management: Unified approach to context-aware logging
To remove duplicated code in your projects:
# Run the integration script
python scripts/integrate_loglama.py --component=your_component_path
# Or for all components
python scripts/integrate_loglama.py --all
This will analyze your codebase, identify duplicated logging code, and replace it with LogLama imports.
Auto-Diagnostic Capabilities
LogLama includes powerful auto-diagnostic tools to help identify and fix common issues in your applications:
Diagnostic Tools
# Run a system health check
python -m loglama.cli diagnose -c health
# Generate a comprehensive diagnostic report
python -m loglama.cli diagnose -c report -o diagnostic_report.json
# Troubleshoot specific components
python -m loglama.cli diagnose -c troubleshoot-logging
python -m loglama.cli diagnose -c troubleshoot-context
python -m loglama.cli diagnose -c troubleshoot-database
Auto-Repair Decorators
LogLama provides smart decorators that can automatically detect and fix common issues:
from loglama.decorators import auto_fix, log_errors, with_diagnostics
# Automatically fix common issues and log errors
@auto_fix
def my_function():
# Your code here
pass
# Log all errors with detailed context
@log_errors
def process_data(data):
# Process data with automatic error logging
pass
# Run diagnostics before and after function execution
@with_diagnostics
def critical_operation():
# Operation will be monitored and diagnosed
pass
Environment Testing
Test LogLama in different environments using the included Ansible playbooks:
# Run all tests locally
cd tests/ansible
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini loglama_test_playbook.yml --limit local
# Test on remote servers
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini loglama_test_playbook.yml --limit remote
Integrating Diagnostics in Your Projects
You can easily integrate LogLama diagnostics into your own projects:
from loglama.diagnostics import check_system_health, generate_diagnostic_report
from loglama.utils.auto_fix import apply_fixes
# Check for issues
health_result = check_system_health()
# Apply automatic fixes if issues are found
if health_result['issues']:
apply_fixes(health_result['issues'])
# Generate a diagnostic report for your application
report = generate_diagnostic_report()
Contributing
We welcome contributions to LogLama. Please see our CONTRIBUTING.md file for details on how to contribute.



